What is it?
Augmented Reality, (AR) defined as technology that superimposes information- sounds, images and text. This information is then displayed in the real world (Emspak, 2018). AR is a concept that is growing rapidly and lies on a “virtual-reality continuum. However, this technology dates back to the 1990s where it was first used in fighter aircrafts to display the altitude, direction and speed of the plane.
One application, in particular, took the world by storm by using augmented reality. Pokémon Go was a global sensation, and at its peak, had over 100 million users. The game allowed users to see Pokémon in the real world through a device (Emspak, 2018). By 2023, the AR market is expected to be worth $61 billion (Fourtańe et al., 2019).
Educational Applicaiton
Schools that implement AR in classrooms will provide students with different learning opportunities and experiences (Fourtańe et al., 2019). These experiences will be engaging, informative and fun. Augmented reality can be used in a variety of subject’s strands. For example, AR can develop students understanding of science, where applications enable students to study the virtual life cycle of butterflies (Bower et al., 2014).
Just like many other technologies, the teacher has the responsibility of being the designer and facilitator. Asking many thought-provoking questions to challenge students (Bower et al., 2014). Teachers need to be confident and have sufficient training regarding augmented reality as many studies show that when used correctly, student’s motivation increases drastically (Bower et al., 2014). When using AR in the classroom, students learning attitudes towards the relevance of learning (Bower et al., 2014).
Human Anatomy 4D
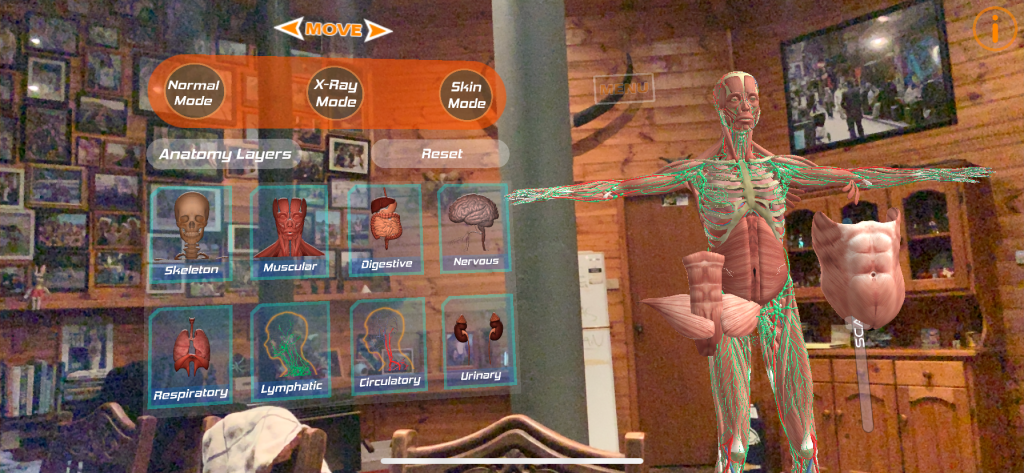
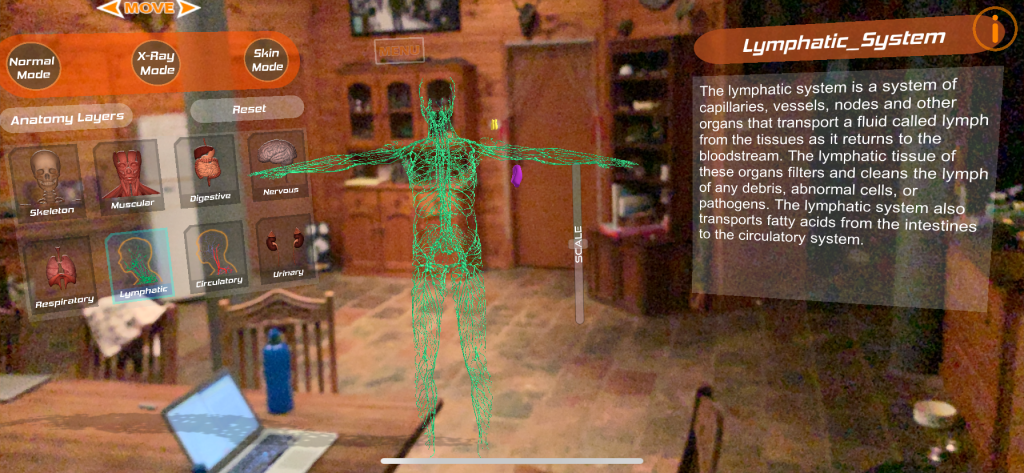
Human Anatomy 4D is a free AR learning tool that I looked at in class. This application allows students to interact with a human body from the comfort of your chair. Users can pull apart the human body and be provided with a detailed description to further understand. The application as a whole is decent. It can be applied in a variety of subjects and can be used in most environments as long as there is a flat space provided. Experiential learning and also explicit instruction can both be applied. However, the application can only be used on Apple devices and the AR function was a little awkward and I had to move further back to get everything on the screen.
References
Bower, M., Howe, C., McCredie, N., Robinson, A., & Grover, D. (2014). Augmented Reality in education – Cases, places and potentials. Educational Media International, 51(1), 1-15.
Emspak, J. (2020). What is Augmented Reality?. livescience.com. Retrieved 1 June 2018, from https://www.livescience.com/34843-augmented-reality.html.
Fourtańe, S., Lang, F., & English, T. (2019). Augmented Reality: The Future of Education. Interestingengineering.com. Retrieved 18 April 2020, from https://interestingengineering.com/augmented-reality-the-future-of-education.





One reply on “Augmented Reality”
Hey Austyn,
I really appreciate the way you clearly outlined AR and used an example that a lot of people would know to complement this.
I also strongly agree about how the reacher still plays the role of a designer and facilitator, and how this means that teachers have to have quality training and confidence when using these resources.
I would love to know what you think about the potential for VR/ The Human anatomy app to facilitate Creativity.
I think that VR as a whole has some great potential for creativity when the students are making the resources to be shown or presented in VR themselves, compared to apps that project pre-made objects (these apps would still be a great classroom tool for learning through promoting engagement).
LikeLike